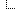Aug 19, 2014, 18:49 pm
![[Image: swarm.jpg]](http://torrentfreak.com/images/swarm.jpg) BitTorrent is one of the fastest and most efficient ways to share large files over the Internet. The popular file-sharing protocol is used by dozens of millions of people every day and accounts for a substantial amount of total Internet traffic.
BitTorrent is one of the fastest and most efficient ways to share large files over the Internet. The popular file-sharing protocol is used by dozens of millions of people every day and accounts for a substantial amount of total Internet traffic. This popularity makes BitTorrent an interesting target for attacks, which various anti-piracy companies have shown in the past. One of these possible attacks was recently unveiled by Florian Adamsky, researcher at the City University London.
In an article published in “Computers & Security” Adamsky and his colleagues reveal an exploit which allows attackers to get a higher download rate from seeders than other people.
In technical terms, the exploit misuses BitTorrent’s choking mechanism of clients that use the “Allowed Fast” extension. Attackers can use this to keep a permanent connection with seeders, requesting the same pieces over and over.
The vulnerability was extensively tested in swarms of various sizes and the researchers found that three malicious peers can already slow download times up to 414.99%. When the number of attackers is greater compared to the number of seeders, the worse the effect becomes.
The impact of the attack further depends on the download clients being used by the seeders in the swarm. The mainline BitTorrent clients and uTorrent are not vulnerable for example, while Vuze, Transmission and Libtorrent-based clients are.
TorrentFreak spoke with Adamsky who predicts that similar results are possible in real swarms. Even very large swarms of more than 1,000 seeders could be affected through a botnet, although it’s hard to predict the precise impact.
“If an attacker uses a botnet to attack the swarm, I think it would be possible to increase the average download time of all peers [of swarms with 1,000 seeders] up to three times,” Adamsky tells us.
“If most of the clients would have a vulnerable client like Vuze or Transmission it would be possible to increase the average download time up ten times,” he adds.
In their paper the researchers suggest a relatively easy fix to the problem, through an update of the “Allowed Fast” extension. In addition, they also propose a new seeding algorithm that is less prone to these and other bandwidth attacks.
Originally Published: Tue, 19 Aug 2014 21:33:00 +0000
source