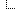Nov 24, 2020, 00:08 am
As the coronavirus pandemic rages across the globe, much of the focus centers on the growing human death toll, which has climbed above one million. But experts caution that a handful of our closest living relatives in the animal kingdom are also in jeopardy from SARS-CoV-2, the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19.
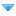
A recent analysis of more than 400 vertebrate species, including birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, predicts that critically endangered primate species such as the northern white-cheeked gibbon, the Sumatran orangutan, and the western lowland gorilla—as well as the endangered chimpanzee and bonobo—are particularly vulnerable to infection due to their genetic similarities to humans.
Study leader Harris Lewin set out to identify animals that might serve as a host for the coronavirus—the ancestor of SARS-CoV-2 is thought to have emerged in a bat species native to China and may have infected another (or more) animal species before crossing over to humans. But as his research progressed, the data began to reveal that humans could be a vector, spreading the disease to wild animals.
As the basis of their study, Lewin and his team looked more closely at the evolution and structure of the protein receptor ACE2, where the coronavirus attaches and subsequently enters human cells. They studied the protein across hundreds of vertebrate species, which allowed them to determine the relative risks of each to contracting the virus.
The researchers examined the type and number of changes at 25 key positions of the ACE2 receptor and created a categorical ranking system ranging from very high to very low risk based on similarities and differences found at those spots. Animals with all 25 positions matching the human protein are thought to be most susceptible. Those predicted to be at very low risk, on the other hand, have ACE2 receptors that are quite different from that of the human.
Among the 103 species that scored as very high, high, or medium risk, 40 percent are classified as threatened on the International Union of Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species, according to the study, published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The 18 very high-risk animals are all Old World primates and great apes. Yet some high-risk endangered species—like the baiji, a freshwater dolphin, Pere David’s deer, and the narrow-ridged finless porpoise whale—surprised the researchers, because they’re distantly related to humans.
The researchers warned against overinterpreting their results, noting that true risk needs to be confirmed with experimental data. And the possibility that infection may occur through a cellular pathway other than ACE2 cannot be ruled out, as there’s more than one way the virus can penetrate the body, Lewin says.
While several species are theoretically susceptible to catching the virus, only a handful of captive animals—domestic dogs, domestic cats, lions, tigers, and minks—have so far been infected, notes Dalen W. Agnew, a professor in the Department of Pathobiology and Diagnostic Investigation at Michigan State University.
In experimental settings, rhesus macaques, cynomolgus macaques, and African green monkeys caught the virus, but most demonstrated relatively mild clinical disease, according to a recent study. Similar studies have shown domestic ferrets have mild or undetectable signs of illness, Egyptian fruit bats show no symptoms, and Syrian hamsters experience mild-to-moderate disease.
Even though the virus does not appear to be as lethal to animals as it is to humans, study co-author Klaus-Peter Koepfli, a research associate at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute, points out that mink can die as a result of contracting SARS-CoV-2.
As it stands, he says there simply isn’t enough information available to fully understand why the virus can lead to increased mortality in some species compared with others. (Buddy, the first dog confirmed with coronavirus, died a few months after his diagnosis, though the exact cause is unknown.)
There’s no evidence that the coronavirus is currently spreading to or within populations of wild animals. Still, some say we probably aren’t aware of all infections similar to the way plenty of human cases have likely gone undetected throughout the pandemic.
Not only are our closest animal kin more susceptible due to genetics, like us their highly social behavior also puts them in peril.
Koepfli notes one animal of concern is Africa’s eastern gorilla, of which fewer than 5,000 remain, divided into small populations and subspecies, including the well-known mountain gorilla. If these great apes, which live in close-knit family groups, became infected and died at similar rates to humans, he adds, it could further endanger the animals.
Because of the ramifications, both Koepfli and Lewin say precautionary measures are key. In settings such as national parks, staff should be regularly tested, because any contact could lead to the beginning of a pandemic in Old World primate species. It is also crucial that zoos continue to carry out their robust management plans to prevent spread from caretakers to animals.
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/anima...-covid-19/
A recent analysis of more than 400 vertebrate species, including birds, fish, amphibians, reptiles, and mammals, predicts that critically endangered primate species such as the northern white-cheeked gibbon, the Sumatran orangutan, and the western lowland gorilla—as well as the endangered chimpanzee and bonobo—are particularly vulnerable to infection due to their genetic similarities to humans.
Study leader Harris Lewin set out to identify animals that might serve as a host for the coronavirus—the ancestor of SARS-CoV-2 is thought to have emerged in a bat species native to China and may have infected another (or more) animal species before crossing over to humans. But as his research progressed, the data began to reveal that humans could be a vector, spreading the disease to wild animals.
Quote:“The potential for COVID-like disease outbreak in either captive or wild populations of endangered primates is pretty high,” says Lewin, distinguished professor of ecology and evolution at University of California, Davis. It’s a particular concern for rare animals in captive settings, similar to the eight infected lions and tigers at the Bronx Zoo in New York City. He says it’s likely they picked up the virus from their human keepers.
Infected humans could transmit the virus in parts of the world where wild animals come in close contact with people, such as in parts of Africa, Lewin cautions.
As the basis of their study, Lewin and his team looked more closely at the evolution and structure of the protein receptor ACE2, where the coronavirus attaches and subsequently enters human cells. They studied the protein across hundreds of vertebrate species, which allowed them to determine the relative risks of each to contracting the virus.
The researchers examined the type and number of changes at 25 key positions of the ACE2 receptor and created a categorical ranking system ranging from very high to very low risk based on similarities and differences found at those spots. Animals with all 25 positions matching the human protein are thought to be most susceptible. Those predicted to be at very low risk, on the other hand, have ACE2 receptors that are quite different from that of the human.
Among the 103 species that scored as very high, high, or medium risk, 40 percent are classified as threatened on the International Union of Conservation of Nature’s Red List of Threatened Species, according to the study, published recently in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The 18 very high-risk animals are all Old World primates and great apes. Yet some high-risk endangered species—like the baiji, a freshwater dolphin, Pere David’s deer, and the narrow-ridged finless porpoise whale—surprised the researchers, because they’re distantly related to humans.
The researchers warned against overinterpreting their results, noting that true risk needs to be confirmed with experimental data. And the possibility that infection may occur through a cellular pathway other than ACE2 cannot be ruled out, as there’s more than one way the virus can penetrate the body, Lewin says.
While several species are theoretically susceptible to catching the virus, only a handful of captive animals—domestic dogs, domestic cats, lions, tigers, and minks—have so far been infected, notes Dalen W. Agnew, a professor in the Department of Pathobiology and Diagnostic Investigation at Michigan State University.
In experimental settings, rhesus macaques, cynomolgus macaques, and African green monkeys caught the virus, but most demonstrated relatively mild clinical disease, according to a recent study. Similar studies have shown domestic ferrets have mild or undetectable signs of illness, Egyptian fruit bats show no symptoms, and Syrian hamsters experience mild-to-moderate disease.
Even though the virus does not appear to be as lethal to animals as it is to humans, study co-author Klaus-Peter Koepfli, a research associate at the Smithsonian Conservation Biology Institute, points out that mink can die as a result of contracting SARS-CoV-2.
As it stands, he says there simply isn’t enough information available to fully understand why the virus can lead to increased mortality in some species compared with others. (Buddy, the first dog confirmed with coronavirus, died a few months after his diagnosis, though the exact cause is unknown.)
There’s no evidence that the coronavirus is currently spreading to or within populations of wild animals. Still, some say we probably aren’t aware of all infections similar to the way plenty of human cases have likely gone undetected throughout the pandemic.
Quote:It is difficult to determine the extent to which the virus is actually spreading to animals, says Andrew Bowman, associate professor in the Department of Veterinary Preventive Medicine at the Ohio State University. “It’s certainly something to keep an eye on,” he says, especially vulnerable populations or those at the human-animal interface.
Not only are our closest animal kin more susceptible due to genetics, like us their highly social behavior also puts them in peril.
Koepfli notes one animal of concern is Africa’s eastern gorilla, of which fewer than 5,000 remain, divided into small populations and subspecies, including the well-known mountain gorilla. If these great apes, which live in close-knit family groups, became infected and died at similar rates to humans, he adds, it could further endanger the animals.
Because of the ramifications, both Koepfli and Lewin say precautionary measures are key. In settings such as national parks, staff should be regularly tested, because any contact could lead to the beginning of a pandemic in Old World primate species. It is also crucial that zoos continue to carry out their robust management plans to prevent spread from caretakers to animals.
https://www.nationalgeographic.com/anima...-covid-19/